What Are the Advantages of Using a Wet Wire Drawing Machine Compared to Dry Drawing Methods?
Wire drawing is a critical industrial process used to reduce the diameter of metal wires, improve mechanical properties, and prepare wire for further applications such as electrical conductors, cables, springs, or structural components. Traditionally, wire drawing can be performed using dry drawing or wet drawing methods. While both techniques achieve diameter reduction and shape control, wet wire drawing machines offer significant advantages over dry methods in terms of efficiency, surface quality, energy consumption, and overall productivity.
This article explores the principles, benefits, and key considerations of wet wire drawing compared to dry drawing methods, providing a detailed guide for engineers, operators, and manufacturers.
1. Understanding Wire Drawing Methods
Dry Wire Drawing
Dry wire drawing involves pulling the wire through a die without the use of significant liquid lubrication. In some cases, minimal solid or paste lubricants may be applied. Dry drawing is typically simpler and less costly in terms of auxiliary equipment.
However, dry drawing has several limitations:
- Higher friction between the wire and die
- Increased heat generation
- Greater risk of surface defects and wire breakage
- More frequent die wear
Wet Wire Drawing
Wet wire drawing uses liquid lubricants or cooling fluids to reduce friction and heat during the drawing process. The wire passes through dies that are submerged or continuously coated with a lubricant, such as oil, emulsion, or water-based lubricants.
Key features include:
- Lubrication: Reduces friction between wire and die
- Cooling: Maintains stable temperature to prevent thermal damage
- Continuous fluid circulation: Ensures uniform lubrication and heat dissipation
By integrating lubrication and cooling, wet wire drawing machines improve wire quality and extend the service life of dies.
2. Reduced Friction and Die Wear
One of the most significant advantages of wet wire drawing is the reduction of friction between the wire and the die:
- Lower Friction: The liquid lubricant forms a thin film between the wire and die surface, reducing metal-to-metal contact.
- Die Longevity: Reduced friction minimizes wear on dies, extending their service life and reducing replacement costs.
- Consistent Diameter: Less friction ensures more uniform wire diameter along its length, critical for high-precision applications.
In contrast, dry drawing produces higher friction, leading to increased heat, accelerated die wear, and more frequent maintenance.
3. Improved Surface Quality of Wires
Surface quality is a key parameter in wire drawing, especially for wires used in electrical, automotive, or high-strength applications. Wet wire drawing provides several benefits in this regard:
- Smoother Surface Finish: Lubrication prevents micro-scratches and surface defects that are common in dry drawing.
- Reduced Oxidation: The fluid layer acts as a barrier against oxidation, improving corrosion resistance.
- Enhanced Coating Compatibility: Smooth wire surfaces improve adhesion of coatings, platings, or insulation materials in subsequent processing steps.
Overall, wet drawing produces wires with superior aesthetics and functional performance compared to dry-drawn wires.
4. Better Heat Dissipation and Temperature Control
Wire drawing generates heat due to plastic deformation and friction. Managing temperature is essential to avoid:
- Die deformation
- Wire breakage
- Surface burning or scaling
Advantages of Wet Drawing in Heat Management:
- Continuous Cooling: The circulating lubricant absorbs and removes heat from the wire and die.
- Stable Process Temperature: Reduces thermal stress on both equipment and wire material.
- Prevention of Metallurgical Damage: Maintaining lower temperatures helps retain mechanical properties of the wire, such as tensile strength and ductility.
Dry drawing, on the other hand, relies on air cooling and limited lubrication, which is less effective for high-speed or large-diameter drawing.
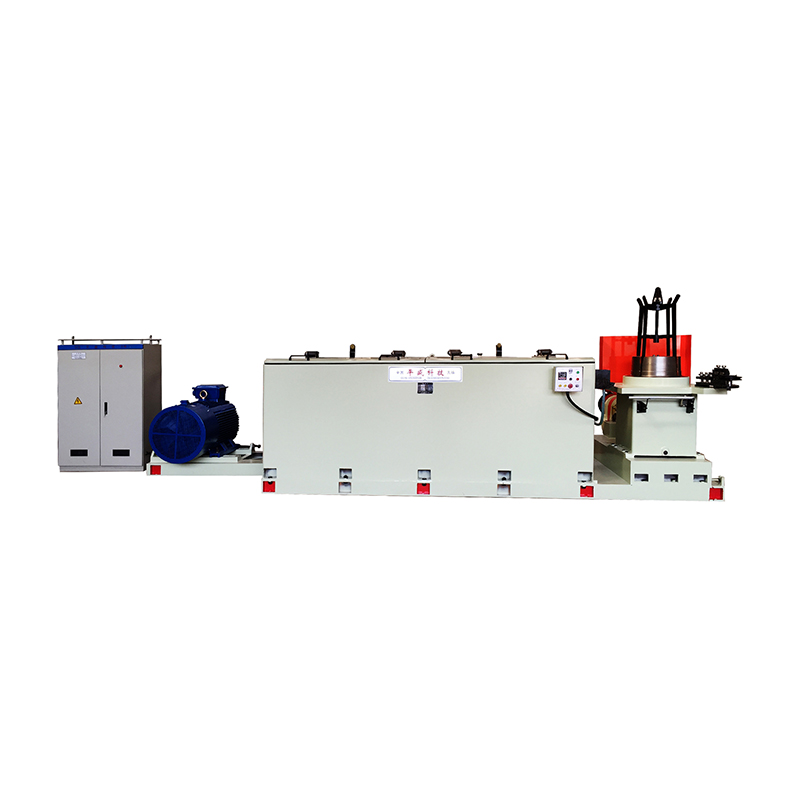
5. Reduced Energy Consumption
Because wet wire drawing reduces friction and maintains lower temperatures, less force is required to pull the wire through the die, resulting in several energy benefits:
- Lower Motor Power Requirements: Machines can operate efficiently at lower torque and energy levels.
- Higher Production Efficiency: Smooth operation reduces downtime caused by wire breaks or die changes.
- Cost Savings: Reduced energy consumption and fewer maintenance interventions lead to lower operating costs.
Dry drawing methods require higher drawing forces, which not only increases energy consumption but also accelerates wear on mechanical components.
6. Increased Wire Speed and Productivity
Wet wire drawing machines support higher wire drawing speeds due to lubrication and heat management:
- Faster Production: Reduced friction allows the machine to operate at higher line speeds without risking wire breakage.
- Continuous Operation: Lubricated dies reduce the frequency of interruptions for maintenance or cooling.
- Higher Throughput: Especially beneficial for high-volume industries, such as copper wire manufacturing, steel wire production, and aluminum cable production.
Dry drawing speeds are limited because higher speeds would increase friction, heat, and the likelihood of defects.
7. Versatility for Different Materials
Wet wire drawing is particularly advantageous when working with high-strength, hard, or brittle metals, such as:
- Copper and Copper Alloys: Common in electrical wires
- Aluminum: Used in power cables and aerospace applications
- Steel and Stainless Steel: High-strength wires for springs, nails, and cables
- Titanium or Specialty Alloys: Used in medical or aerospace components
Lubrication in wet drawing ensures uniform deformation and reduces the risk of cracking or surface damage for these challenging materials. Dry drawing may be limited to softer metals or lower-strength alloys.
8. Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
Because wet wire drawing reduces die wear and wire breakage, machines experience fewer operational interruptions:
- Longer Die Life: Lubrication prevents abrasive wear and reduces the frequency of die replacement.
- Less Wire Scrap: Improved surface quality and fewer breaks mean lower material wastage.
- Simplified Cleaning: Lubricants can help prevent residue build-up and keep the machine components cleaner.
In comparison, dry drawing machines require more frequent inspections, die replacements, and downtime for repairs, reducing overall productivity.
9. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Modern wet wire drawing systems often use emulsions or biodegradable lubricants, which can minimize environmental impact compared to older oil-based systems. Additionally:
- Reduced Dust Generation: Wet drawing produces fewer airborne particles than dry drawing, improving workplace safety.
- Temperature Safety: Lower operating temperatures reduce the risk of burns or heat-related accidents.
- Cleaner Work Environment: Lubricated surfaces minimize wire dust and debris accumulation.
Dry drawing can generate dust and heat, which may require additional ventilation, cleaning, and safety precautions.
10. Cost-Benefit Considerations
While wet wire drawing machines require an initial investment in lubrication systems, pumps, and cooling circuits, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs:
- Lower Scrap Rate: Fewer wire defects reduce material waste.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Extended die life and fewer repairs save money over time.
- Higher Output: Increased speed and efficiency enhance profitability.
- Improved Product Quality: Higher-quality wire commands premium pricing, particularly in electrical and industrial applications.
Dry drawing may appear cheaper initially but incurs higher costs from scrap, die wear, and downtime.
11. Summary of Advantages
| Feature | Wet Wire Drawing | Dry Wire Drawing |
| Friction | Low due to lubrication | High, leading to wear |
| Heat Generation | Minimal, cooling fluid removes heat | High, risk of overheating |
| Surface Quality | Smooth, defect-free | Rougher, more scratches |
| Die Life | Extended | Shorter due to wear |
| Wire Speed | High | Limited |
| Material Versatility | High, suitable for hard/brittle metals | Limited to softer materials |
| Maintenance | Less frequent, easier | Frequent, more intensive |
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Safety & Environment | Reduced dust, cooler operation | Dust generation, higher temperature risk |
Conclusion
Wet wire drawing machines provide substantial advantages over dry drawing methods in modern industrial wire production. By integrating lubrication and cooling, wet drawing reduces friction, heat generation, and die wear, resulting in improved wire quality, higher production speeds, and longer equipment life. The method is especially suitable for high-strength, brittle, or chemically sensitive metals, and it enhances safety and environmental conditions in the workplace.
Although wet wire drawing requires a higher initial investment for lubrication and cooling systems, the long-term benefits—reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance costs, increased productivity, and superior wire quality—make it the preferred choice for manufacturers seeking high efficiency and consistent results.
For industries aiming to produce high-quality wire at scale, wet wire drawing is not just an option but a strategic investment in productivity, safety, and product performance.

 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español Français
Français Português
Português عربى
عربى