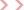
Key Maintenance Requirements for Wet Wire Drawing Machines
Wet wire drawing machines are essential in the metalworking industry for producing fine, high-precision wires used in cables, springs, welding electrodes, and other applications. Unlike dry drawing, wet wire drawing involves lubricating the wire with a liquid coolant to reduce friction, improve surface finish, and extend die life.
However, these machines require strict maintenance to ensure efficiency, longevity, and consistent wire quality. This article explores the key maintenance requirements for wet wire drawing machines, including lubrication management, die care, mechanical inspections, and troubleshooting common issues.
1. Importance of Regular Maintenance in Wet Wire Drawing
Neglecting maintenance can lead to:
Increased downtime due to breakdowns.
Poor wire quality (surface defects, inconsistent diameter).
Higher energy consumption from inefficient operation.
Premature die wear, increasing replacement costs.
A well-maintained machine ensures:
Longer die lifespan
Stable drawing speed & tension
Reduced power consumption
Consistent wire quality

2. Key Maintenance Requirements
A. Lubrication & Coolant Management
Since wet drawing relies on liquid lubrication, maintaining the coolant system is critical.
1. Coolant Quality Control
Check concentration (usually 5-10% emulsified oil in water).
Monitor pH levels (should be neutral to prevent corrosion).
Remove metal fines & contaminants using filters or magnetic separators.
2. Lubrication System Maintenance
Inspect pumps & nozzles for clogging.
Ensure proper flow rate to all dies.
Replace old coolant every 3-6 months to prevent bacterial growth.
B. Die Maintenance & Inspection
Wire drawing dies (typically tungsten carbide or diamond) wear out over time.
1. Regular Die Inspection
Measure wire diameter (if inconsistent, dies may be worn).
Check for scratches or cracks in the die surface.
Use a microscope for fine inspection.
2. Die Cleaning & Polishing
Ultrasonic cleaning removes embedded particles.
Polishing (for tungsten carbide dies) restores smoothness.
3. Proper Die Storage
Keep dies in dry, dust-free containers when not in use.
Avoid impact or mishandling to prevent cracks.
C. Mechanical System Checks
1. Tension Control System
Calibrate tension sensors regularly.
Check capstans & pulleys for wear.
2. Drive Motor & Gearbox
Lubricate bearings & gears (use high-temperature grease).
Monitor vibration & noise (indicates misalignment or wear).
3. Wire Guide & Alignment
Ensure proper alignment to prevent uneven die wear.
Replace worn guides to avoid wire surface damage.
D. Electrical & Control System Maintenance
Inspect wiring & connections for corrosion.
Test emergency stop functions.
Update PLC/software (if applicable).
3. Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Task Frequency
Coolant quality check Daily
Die inspection Weekly
Lubrication system cleaning Monthly
Tension system calibration Quarterly
Full mechanical inspection Biannually
Coolant replacement Every 3-6 months
4. Common Problems & Troubleshooting
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Wire breaks | Worn dies, excessive tension | Replace dies, adjust tension |
| Poor surface finish | Dirty coolant, misalignment | Filter coolant, realign guides |
| Overheating | Insufficient lubrication | Check coolant flow, clean nozzles |
| Vibration/noise | Loose belts, bearing wear | Tighten belts, replace bearings |
5. Best Practices for Extending Machine Life
Use high-quality dies & lubricants.
Train operators on proper handling.
Keep logs of maintenance activities.
Store spare parts (dies, seals, filters) for quick replacements.
6. Future Trends in Wet Wire Drawing Maintenance
IoT-enabled monitoring for real-time wear detection.
Automated lubrication systems for precision control.
AI-based predictive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime.
Proper maintenance of wet wire drawing machines is essential for efficiency, wire quality, and cost control. By following a structured maintenance schedule—focusing on coolant management, die care, mechanical checks, and troubleshooting—operators can maximize machine lifespan and productivity.
Key Takeaways:
Monitor coolant quality & cleanliness.
Inspect dies regularly for wear.
Maintain proper tension & alignment.
Follow a preventive maintenance schedule.

 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español Français
Français Português
Português عربى
عربى