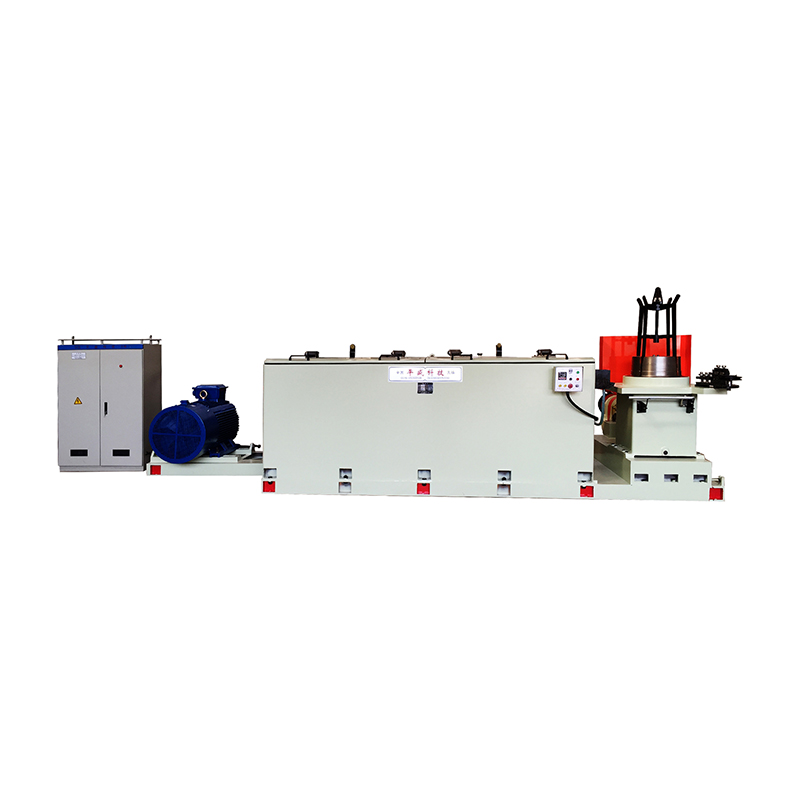
How to Choose the Right Wet Wire Drawing Machine for Your Wire Production Needs?
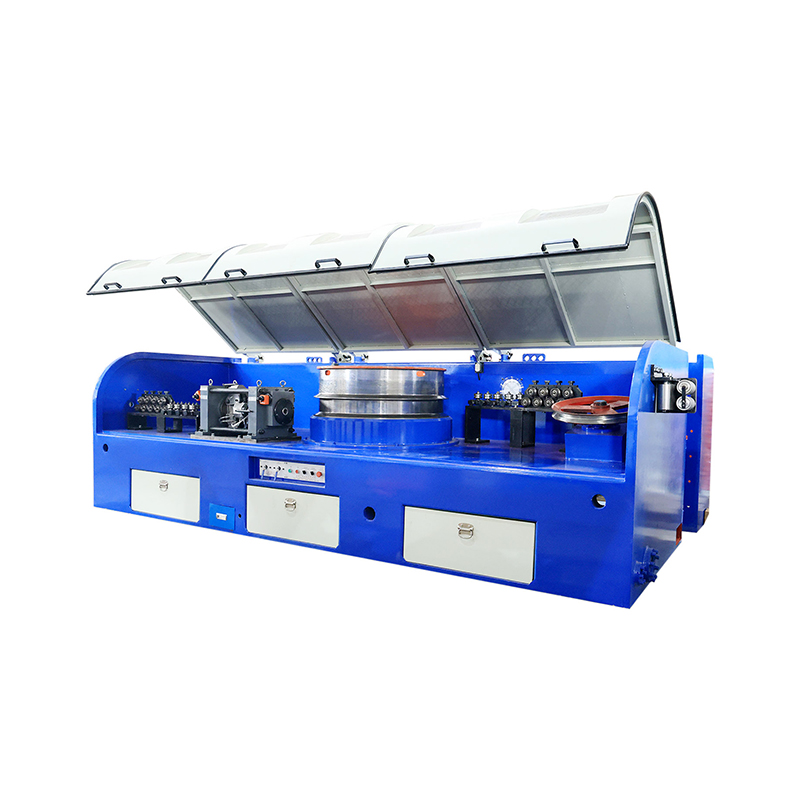
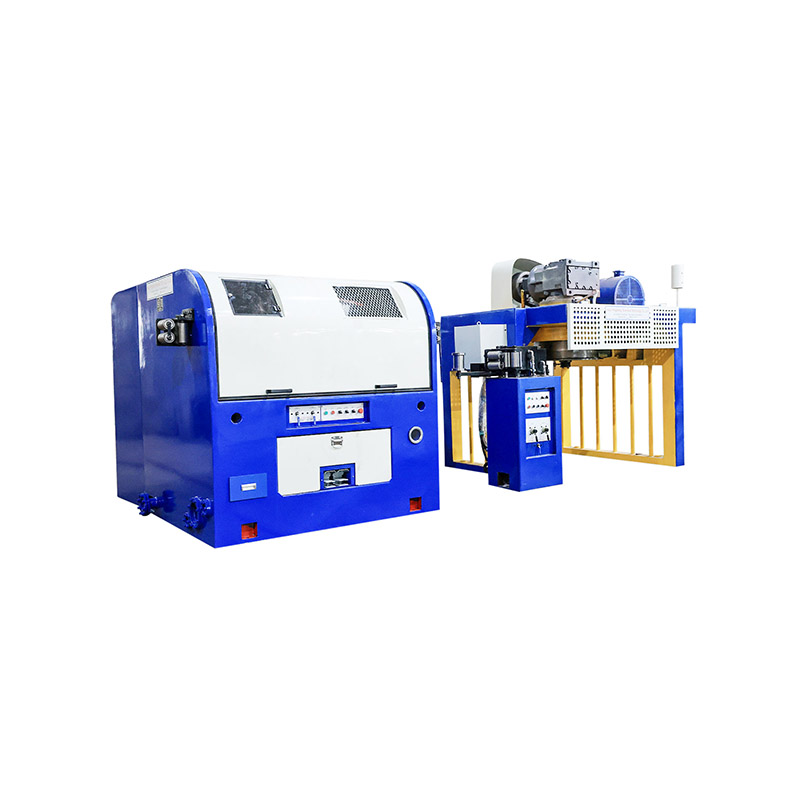
A wet wire drawing machine is specialized equipment used to reduce wire diameter by pulling metal wire through a series of drawing dies while the wire and dies are immersed in a lubricant or coolant. This wet drawing process reduces friction, controls heat generation, and improves surface quality, making it especially suitable for fine and ultra-fine wire production.
Wet wire drawing machines are commonly used in the production of copper, aluminum, brass, steel, and alloy wires for applications such as electrical conductors, welding wire, cables, springs, and precision components. Choosing the right machine is critical to achieving consistent wire quality, high productivity, and long-term operational stability.
Define Your Wire Material and Application Requirements
The first step in selecting a wet wire drawing machine is understanding the material you plan to process and its final application. Different metals have varying tensile strengths, ductility, and lubrication requirements. Copper and aluminum are softer and more conductive, while steel and alloy wires demand higher drawing forces and more robust machine structures.
Application requirements such as electrical conductivity, surface finish, and mechanical strength also influence machine selection. For example, wire intended for electrical cables requires excellent surface smoothness and dimensional consistency, while welding wire production prioritizes strength and uniformity.

Wire Diameter Range and Reduction Ratio
Wire diameter range is a critical factor when choosing a wet wire drawing machine. Machines are designed to handle specific inlet and outlet wire sizes, and exceeding these limits can compromise performance or cause excessive wear. Fine wire applications often require multiple drawing passes with precise control over reduction ratios.
The reduction ratio per die affects wire quality and die life. A properly selected machine allows balanced reductions across multiple capstans or blocks, minimizing stress on the wire while maintaining efficient production rates.
Typical Wire Size Considerations
- Inlet wire diameter compatibility
- Minimum achievable final wire diameter
- Maximum allowable reduction per pass
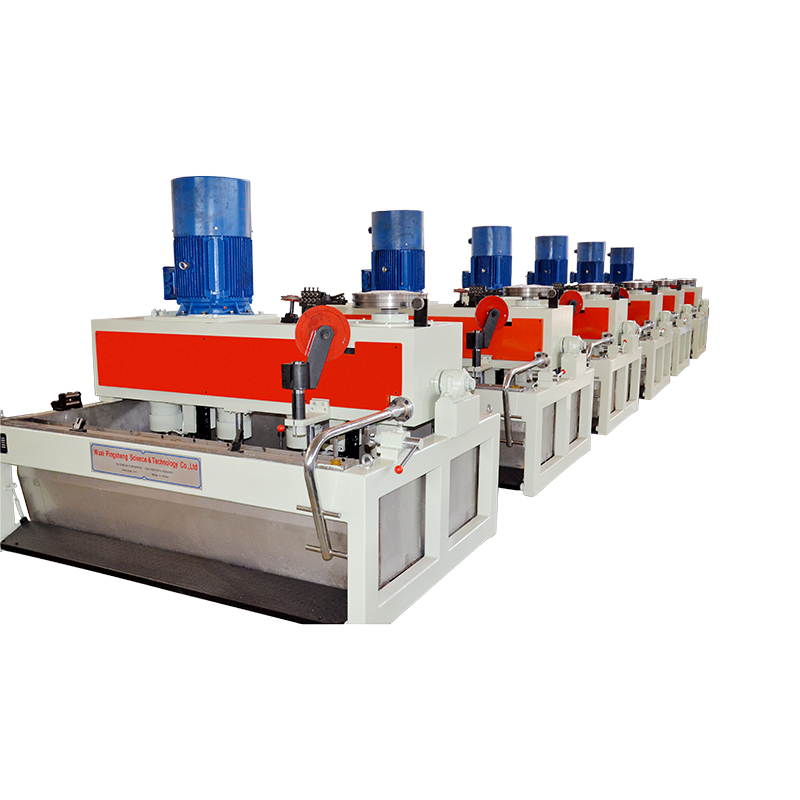
Number of Drawing Blocks and Machine Configuration
Wet wire drawing machines are available with different numbers of drawing blocks or capstans, depending on production requirements. More blocks allow for smaller reductions per pass, which improves wire quality and reduces breakage, especially for fine and sensitive materials.
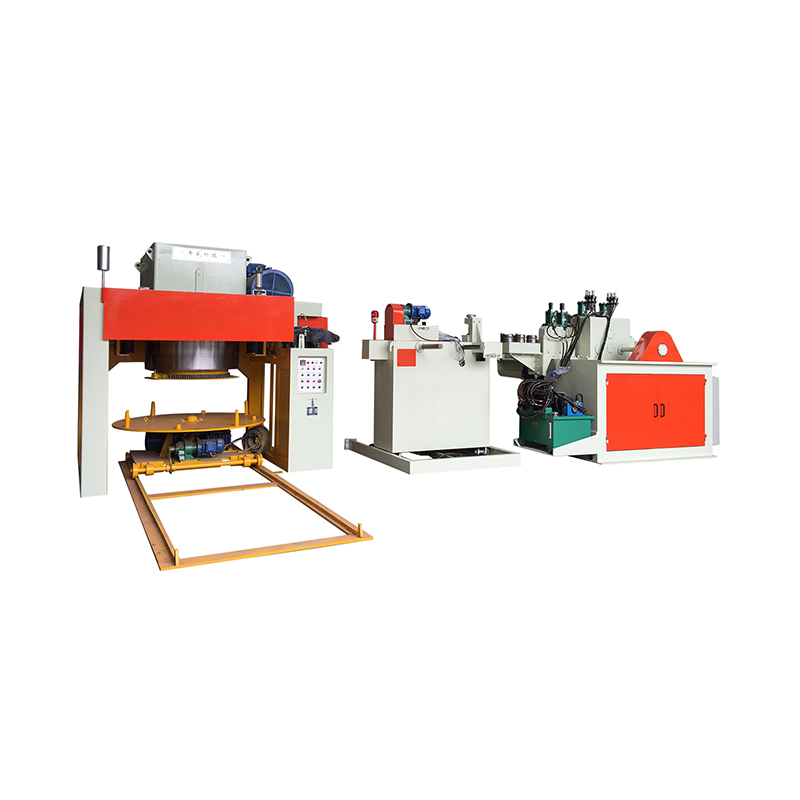
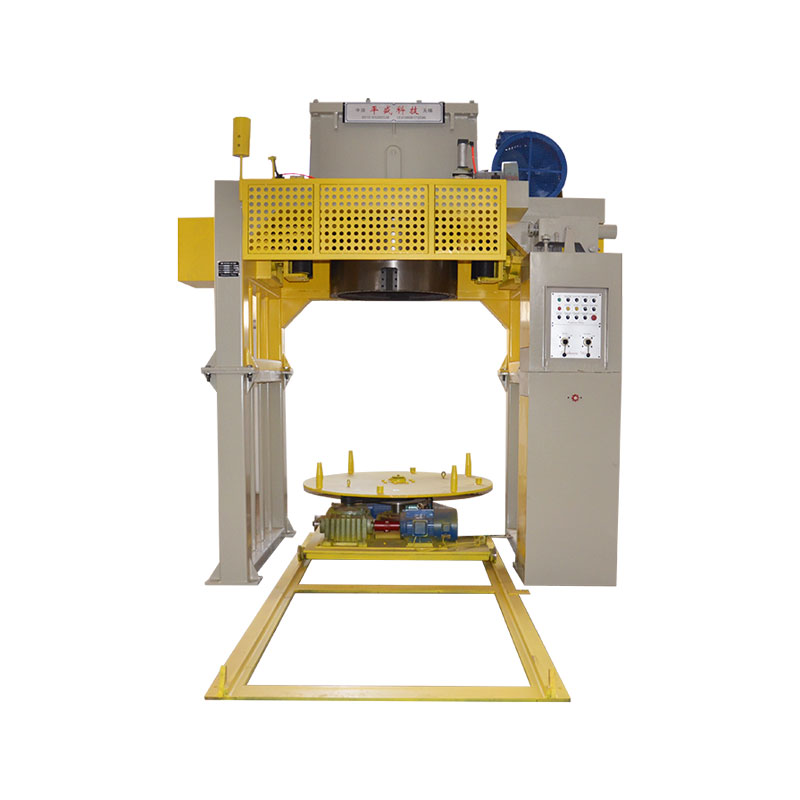
Machine configuration also determines layout efficiency and maintenance accessibility. Vertical and horizontal designs each offer advantages depending on factory space, operator workflow, and integration with upstream and downstream equipment.
Lubrication and Cooling System Performance
The lubrication system is the core advantage of wet wire drawing. Proper lubrication reduces friction between the wire and dies, minimizes heat buildup, and extends die life. When selecting a machine, it is important to evaluate the design of the lubrication circulation and filtration system.
An effective cooling system ensures stable drawing conditions even at high speeds. Machines with well-designed coolant flow and temperature control deliver more consistent wire quality and reduce the risk of surface defects.
Key Lubrication System Features
- Continuous lubricant circulation
- Effective filtration to remove metal particles
- Temperature control for stable operation
Production Speed and Output Capacity
Production speed directly impacts output capacity and overall manufacturing efficiency. Wet wire drawing machines are often selected for their ability to operate at higher speeds while maintaining surface quality. However, maximum speed must be balanced with wire material properties and final diameter requirements.
Choosing a machine with adjustable speed control allows operators to optimize performance for different wire sizes and materials. This flexibility is especially valuable for manufacturers producing multiple wire types on the same line.
Automation, Control Systems, and Monitoring
Modern wet wire drawing machines increasingly incorporate automated control systems to improve consistency and reduce operator dependency. Features such as tension control, speed synchronization, and real-time monitoring help maintain stable drawing conditions.
Advanced machines may also include fault detection and data logging, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization. These capabilities contribute to reduced downtime and improved production reliability.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Energy consumption is a significant operating cost in wire drawing operations. Efficient motor design, optimized transmission systems, and effective lubrication all contribute to reduced power usage. When evaluating machines, it is important to consider not only initial purchase cost but also long-term operating expenses.
Machines designed for energy efficiency often deliver better return on investment through lower utility costs and reduced maintenance requirements over their service life.
Maintenance, Durability, and Service Support
A wet wire drawing machine is a long-term investment, so durability and ease of maintenance are key selection criteria. High-quality materials, precision manufacturing, and robust structural design ensure stable operation under continuous production conditions.
Equally important is the availability of technical support, spare parts, and after-sales service. Reliable support minimizes downtime and helps maintain consistent production quality over time.
Comparing Wet and Dry Wire Drawing Machines
| Aspect | Wet Wire Drawing | Dry Wire Drawing |
| Lubrication | Liquid-based immersion | Solid or powder lubricant |
| Wire Size | Fine and ultra-fine wires | Medium to large wires |
| Surface Quality | Very smooth | Moderate |
Making the Final Selection Decision
Selecting the right wet wire drawing machine requires a comprehensive evaluation of material characteristics, wire size range, production capacity, lubrication performance, and automation level. Matching machine capabilities with actual production needs ensures consistent quality and efficient operation.
By focusing on practical performance factors rather than generic specifications, manufacturers can choose a wet wire drawing machine that delivers reliable results, long service life, and strong economic value for their wire production operations.

 EN
EN
 English
English Español
Español Français
Français Português
Português عربى
عربى